





The Anytime You Drink Vitamin® Bottle
The Anytime You Drink Vitamin® Bottle
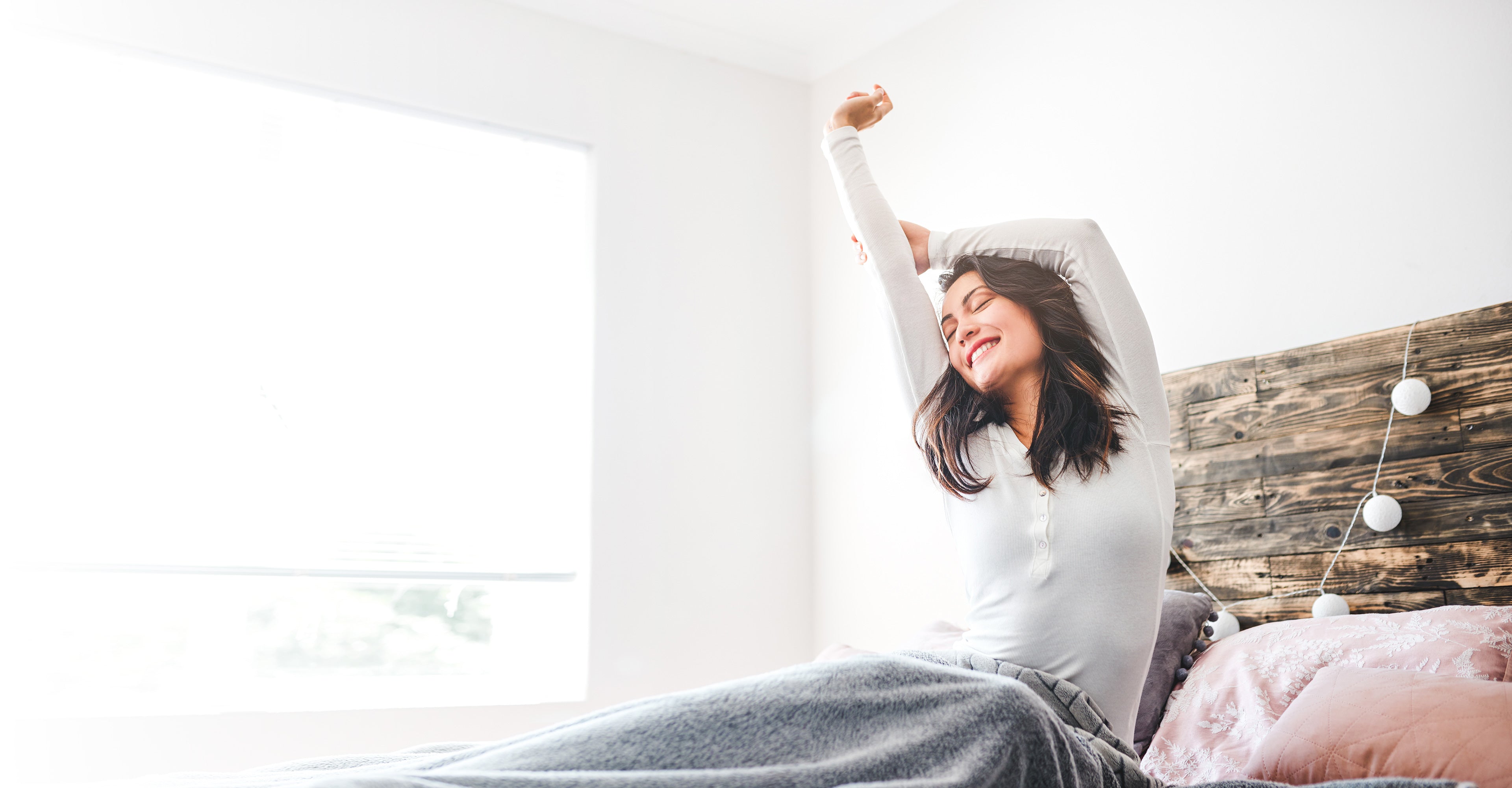
Doctor-developed chewables that support alcohol metabolism, promote liver health, and restore vital nutrients, so you can wake up feeling better than you should.
Vegan, Gluten-Free, Sugar-Free, Zero Calories, Zero Carbs
If you’re not fully satisfied, simply let us know within 30 days and we’ll refund you.







Supplement Facts
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) | 140mg | 156% |
| Vitamin E (as D-Alpha Tocopheryl Succinate) | 2.01mg | 14% |
| Thiamin (Thiamin HCI) | 0.45mg | 38% |
| Riboflavin | 9.5mg | 730% |
| Niacin | 10.8mg NE | 64% |
| Vitamin B6 (as Pyridoxal-5-Phosphate) | 18mg | 1,058% |
| Folate (as L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate Calcium) | 600mcg DFE | 150% |
| Vitamin B12 (as Methylcobalamin) | 16.8mcg | 700% |
| Pantothenic Acid (as Calcium-D-Pantothenate) | 12mg | 240% |
| Magnesium (as Magnesium Glycinate) | 10mg | 2% |
| Zinc (as Zinc Bisglycinate Chelate) | 0.34mg | 4% |
| Potassium (as Potassium Citrate) | 19mg | <1% |
| Proprietary Liver Support Blend* Silymarin (From Milk Thistle Seed Extract), Taurine, Dihydromyricetin (DHM), L-Glutathione |
383.75mg | ** |
| ** Daily Value not established |

How It Works
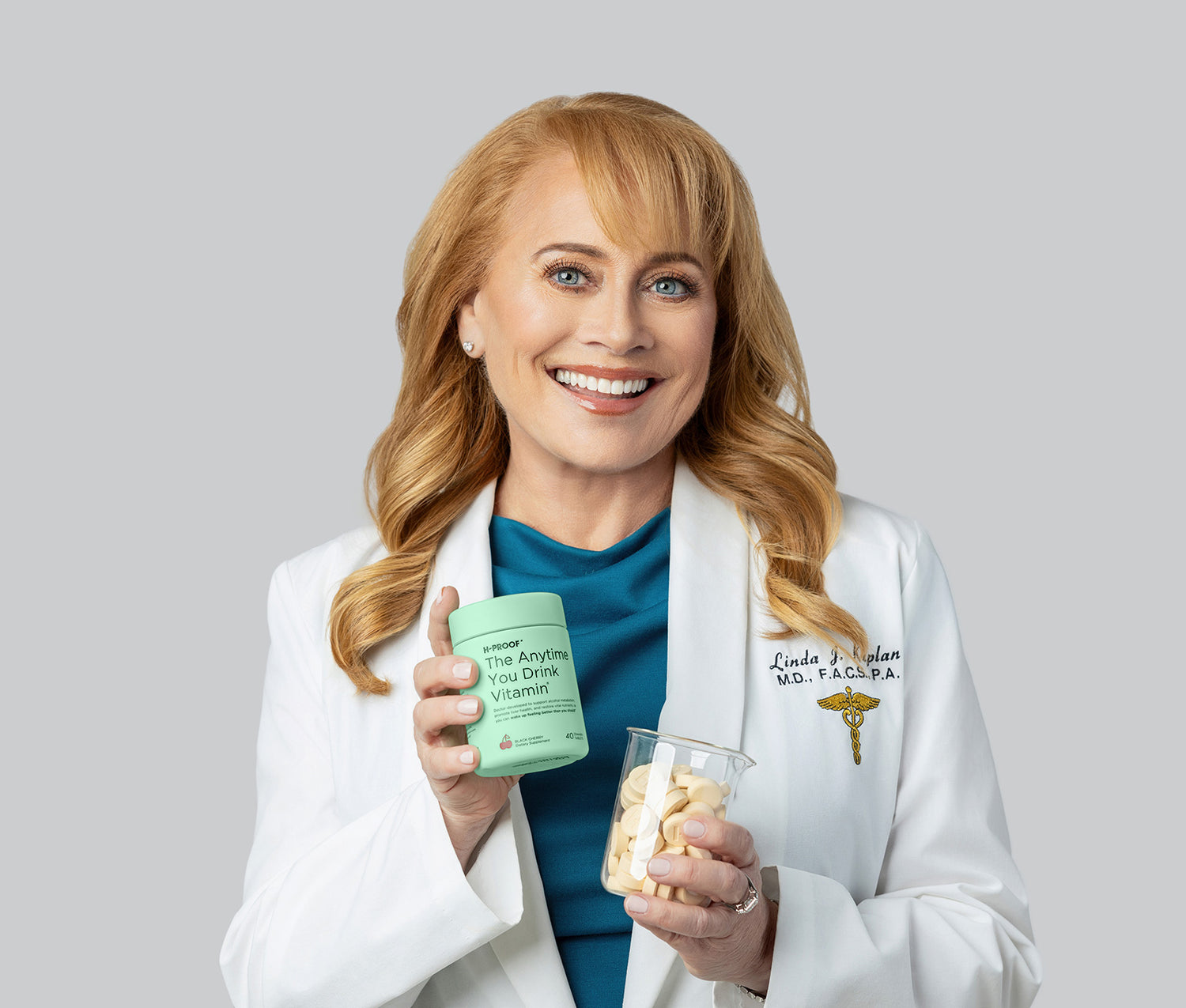
How It Works
Do you ever have a few drinks and wake up feeling a little rough? Alcohol metabolism is the key, not dehydration.
Developed by board-certified physician Dr. Linda J. Kaplan, MD, The Anytime You Drink Vitamin's patented formula combines 16 active ingredients to help you metabolize alcohol the right way so you can wake up feeling fresh*

3 Simple Steps
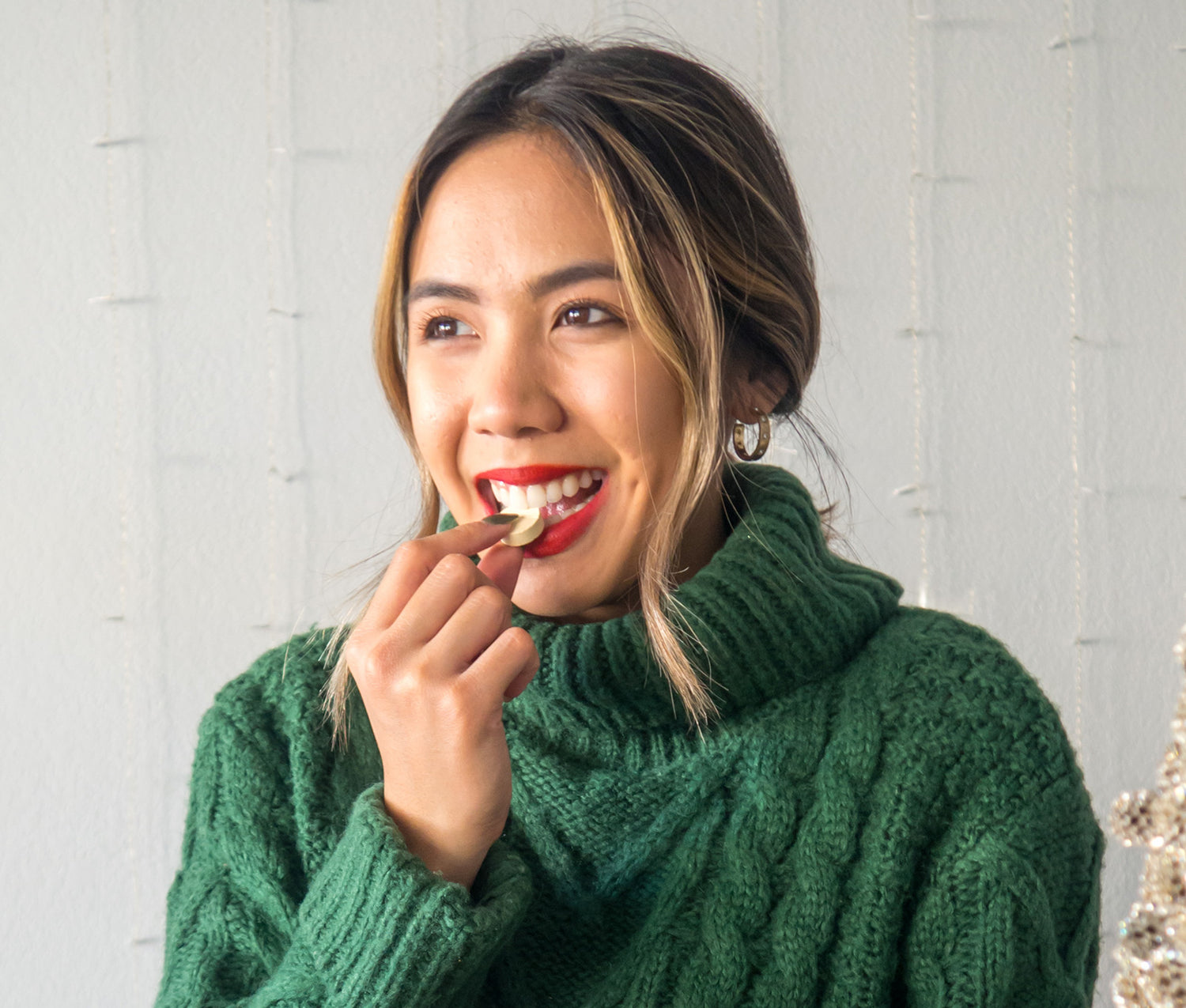
3 Simple Steps
-
Enjoy your drinks
-
Chew 2 Vitamins
-
Wake up feeling better than you should*
Science-Supported Ingredients
Vitamin C & Zinc
Support the immune system and cellular health*
B Vitamins
Promote enzymes that power alcohol metabolism*
Electrolytes
Hydrate and help rebalance the brain, heart, and body*
Liver Supporters
Promote healthy liver function and metabolism*
Antioxidants
Support the body's natural defenses against free radicals*
Supplement Facts
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) | 140mg | 156% |
| Vitamin E (as D-Alpha Tocopheryl Succinate) | 2.01mg | 14% |
| Thiamin (Thiamin HCI) | 0.45mg | 38% |
| Riboflavin | 9.5mg | 730% |
| Niacin | 10.8mg NE | 64% |
| Vitamin B6 (as Pyridoxal-5-Phosphate) | 18mg | 1,058% |
| Folate (as L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate Calcium) | 600mcg DFE | 150% |
| Vitamin B12 (as Methylcobalamin) | 16.8mcg | 700% |
| Pantothenic Acid (as Calcium-D-Pantothenate) | 12mg | 240% |
| Magnesium (as Magnesium Glycinate) | 10mg | 2% |
| Zinc (as Zinc Bisglycinate Chelate) | 0.34mg | 4% |
| Potassium (as Potassium Citrate) | 19mg | <1% |
| Proprietary Liver Support Blend* Silymarin (From Milk Thistle Seed Extract), Taurine, Dihydromyricetin (DHM), L-Glutathione |
383.75mg | ** |
| ** Daily Value not established |
Feel Good, Guaranteed
Because everybody is different, we want you to try H-PROOF risk-free! If you’re not fully satisfied with your first purchase of the Drink Vitamin, Energy Vitamin, or both, simply let us know within 30 days, and we’ll refund you 100% (terms apply)
-
-
-
Featured In
FAQs
View All FAQs
How does it work?
The Anytime You Drink Vitamin® supports alcohol metabolism, promotes liver health, and restores vital nutrients, so you can wake up feeling better than you should*
When should I take it?
In general, we recommend chewing 2 tablets ASAP after your last drink.
However, everybody is different, and you may want to experiment to figure out how The Anytime You Drink Vitamin® works best for you!
Why is it $2.95/serving?
The Anytime You Drink Vitamin® is $2.95 per serving because it utilizes the most bioavailable form of each of its 16 active ingredients, is made in the USA, and is patented -- all things that require significant investment. If we made it less expensively, we would have to compromise on many of those factors, which we are unwilling to do.
As a doctor-owned business, safety and quality have always been our top priorities.
We offer a 30 day money back guarantee so that you can experience it risk-free before deciding whether or not you like it. We'd love for you to give it a try!
How does the body metabolize alcohol?
The body primarily metabolizes alcohol in the liver using a series of enzymatic processes. The key enzymes and steps involved include:
- Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH): Converts alcohol (ethanol) into acetaldehyde, a toxic compound.(1)
- Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH): Converts acetaldehyde into acetate, which is then broken down into water and carbon dioxide for elimination.(1)
Other enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) and catalase, play minor roles, especially after heavy drinking.(1)
Source:
(1) Alcohol Metabolism | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/alcohol-metabolism
What influences alcohol metabolism?
Alcohol metabolism in humans is a complex process influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, physiological, and lifestyle factors:
- Genes (ADH & ALDH): Some people carry ALDH2 variants that clear acetaldehyde more slowly, causing flushing, nausea, or quick intoxication.(2,3)
- Food and Diet: Eating—especially carbs and protein—slows alcohol absorption, lowering peak blood‑alcohol levels.(2,4) Certain foods (like tomatoes) may even speed metabolism by boosting pyruvate.(5)
- Enzyme Activity and Induction: Heavy, regular drinking can ramp up CYP2E1. Alcohol may clear faster, but more toxic by‑products and oxidative stress build up, straining the liver.(6,7)
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors: Factors such as age, sex, body weight, and overall health status influence alcohol metabolism. For example, women often have lower levels of gastric ADH, leading to higher blood alcohol concentrations compared to men after consuming the same amount of alcohol. Physical activity, medications, and concurrent substance use can also modulate enzyme activity and alcohol breakdown.(2)
Sources:
(2) Genetic and environmental influences on alcohol metabolism in humans. National Library of Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11198709/
(3) An assessment of the genetic relationship between alcohol metabolism and alcoholism risk in Australian twins of European ancestry. National Library of Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10857251/
(4) Alcohol metabolism at moderate drinking in healthy men. Comparison between differences of alcohol beverages, with and without meal, and genetic polymorphism. National Library of Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21861333/
(5) Aqueous Components of Tomato Accelerate Alcohol Metabolism by Increasing Pyruvate Level. Scientific Research Publishing. https://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation?paperid=45556
(6) The role of CYP2E1 in alcohol metabolism and sensitivity in the central nervous system. National Library of Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23400924/
(7) Ethanol oxidizing enzymes: roles in alcohol metabolism and alcoholic liver disease. National Library of Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9224501/
What is the best vitamin to take for your liver?
Your liver works best with a full team of nutrients, so we pack a lineup of science‑backed vitamins into The Anytime You Drink Vitamin® for well‑rounded liver support:
- B Vitamins (especially B12 and Folate): These are essential for overall liver function and help in the metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.(8) They also play a role in reducing homocysteine levels, which, when elevated, can be harmful to the liver.(9)
- Vitamin C: As an antioxidant, vitamin C helps protect liver cells from oxidative stress and may support liver health.(10)
- Vitamin E: Often highlighted for its antioxidant properties, vitamin E has been shown through multiple clinical studies to lower harmful liver enzymes and ease fat‑related irritation.(11)
Sources:
(8) B Vitamins: Functions and Uses in Medicine. National Library of Medicine. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9662251/
(9) B Vitamins, Homocysteine and Bone Health. National Library of Medicine. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4425139/
(10) Hepatoprotective Effect of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid). Scientific Research Publishing. https://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation?paperid=27508
(11) Vitamin E improves serum markers and histology in adults with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. National Library of Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39150005/

